Delayed (after) transitions
Delayed transitions are transitions that only happen after a set amount of time. Delayed transitions are handy for building timeouts and intervals into your application logic. If another event occurs before the end of the timer, the transition doesn’t complete.
Delayed transitions are defined on the after property in milliseconds. They are often referred to as “after” transitions.
import { createMachine } from 'xstate';
const pushTheButtonGame = createMachine({
initial: 'waitingForButtonPush',
states: {
waitingForButtonPush: {
after: {
5000: {
target: 'timedOut',
actions: 'logThatYouGotTimedOut',
},
},
on: {
PUSH_BUTTON: {
actions: 'logSuccess',
target: 'success',
},
},
},
success: {},
timedOut: {},
},
});
↓Jump to learning more about delays in XState↓
View this machine in Stately Studio.
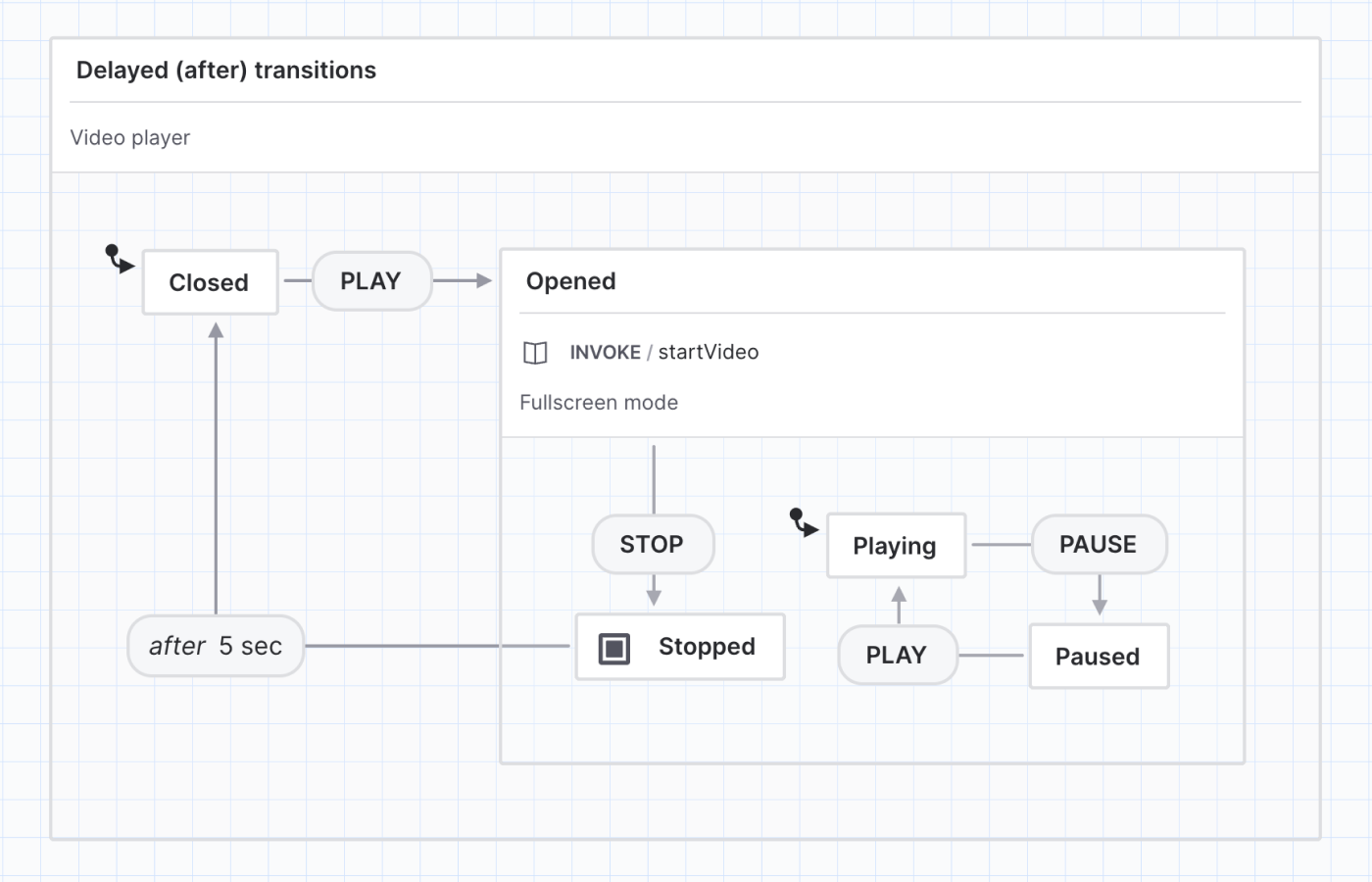
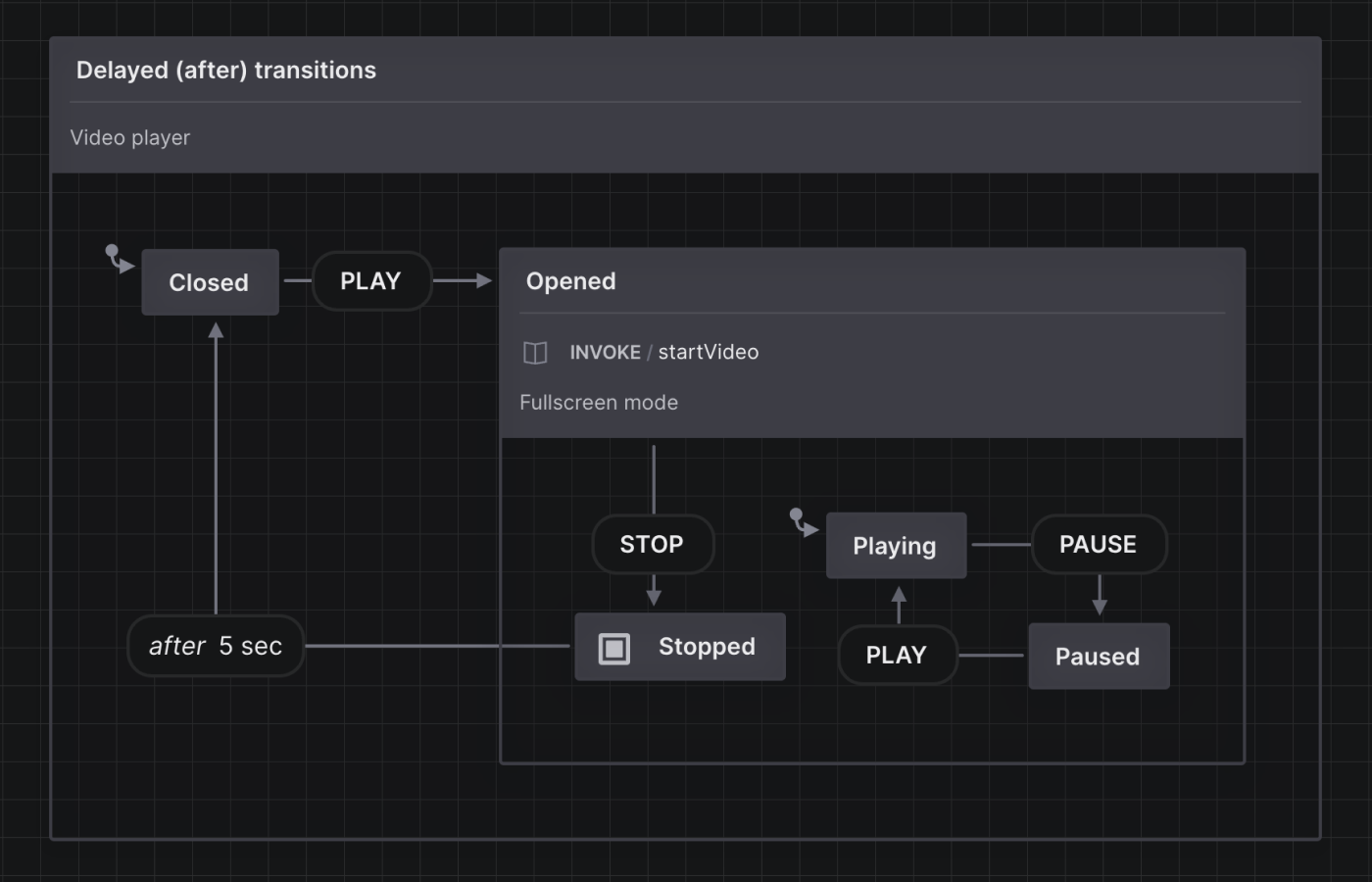
In a video player, want the video to be Closed out of fullscreen mode a few seconds after the video has Stopped, instead of closing the fullscreen mode suddenly as soon as the video is stopped. The eventless transition above transitions from the Stopped state to the Closed state after 5 seconds.
Using delayed transitions in Stately Studio
In Stately Studio, delayed transitions are labeled “after.”
Make an event into a delayed transition
First, select the event you want to replace with a delayed transition. Then…
Using the quick actions menu
- Right-click the event to bring up the quick actions menu.
- Choose After from the Event type options.
- Use the Transition details panel to change the delay time.
Using the Transition details panel
- Open the Transition details panel from the right tool menu.
- Choose After from the Event type dropdown menu.
- Specify the delay time in milliseconds using the Delay text input.
Delays
You can define delays in a few ways: inlined, referenced, and as an expression.
Inlined delays
You can define an inlined delay by specifying the delay time (in milliseconds) directly:
const machine = createMachine({
initial: 'idle',
states: {
idle: {
after: {
1000: { target: 'nextState' },
},
},
nextState: {},
},
});
This will transition to the nextState state after 1000ms.
Referenced delays
You can also define referenced delays by specifying a string delay key, and providing the actual delay time separately.
For example:
const machine = createMachine(
{
initial: 'idle',
states: {
idle: {
after: {
timeout: { target: 'nextState' },
},
},
nextState: {},
},
},
{
delays: {
timeout: 1000,
},
},
);
Delay expressions
The delay option can be evaluated as a delay expression. The delay expression function takes in an object that contains context and event properties and returns the resolved delay (in milliseconds).
`after: [{ delay: () => 1000, target: ... }]`;
Lifecycle
Delayed transition timers are canceled when the state is exited.
Testing
- Simulated clock
TypeScript
Coming soon
Cheatsheet
Use our XState delayed transitions cheatsheet below to get started quickly.
createMachine({
after: {
DELAY: {
/* ... */
},
},
}).provide({
delays: {
DELAY: 1000, // or expression
},
});